Random Number Generator In Java
Often we have to generate random numbers during the implementation of a program in Java. There are different ways to do that which is listed below. We can generate a random number in Java by using built-in methods and classes.
- One of the most important ways to generate a random number in Java is java.util.Random class
- We can also generate random numbers of type double with Math.Random () method
- ThreadLocalRandom class
Let’s analyze them one by one.
Generate Random Numbers Using Java.util.Random class
This class is used to generate a stream of pseudo-random numbers and the instances of this particular class are considered as thread safe. In this class we can generate different random data types, i.e. float, int, double.
This class has two constructors (a) Random(), it creates a new random number generator and (b) Random(long seed), which creates random number using a single long seed.
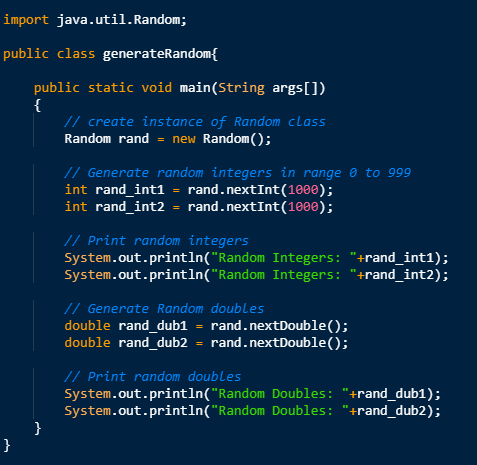
- If we want to generate random number using this class then we have to create an instance of that class first and then invoke these methods: nextInt(), nextDouble(), nextLong.
- We have the facility to generate random number of types: float, int, double, long, boolean
- To place an upper bound on the range of random number, we pass arguments to the method for that purpose. Such that, nextInt(6) will generate numbers between the range of 0 to 5 (both inclusive).
Following program demonstrates random number generation using java.util.Random class.
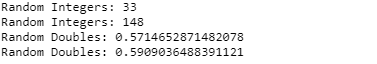
Output:
Generate Random Numbers Using Math.Random () Method
This particular method will return a pseudo-random double type value with a positive sign, greater than or equal to 0.0 and less than 1.0. When this method is invoked, it will create a pseudo-random number generator and therefore is called afterward for all the calls towards this method and cannot be used anywhere else.
- Math class includes various methods to perform various operations which includes: calculation, exponentiation, logarithms etc.
- Random() is a method of Math class and it returns double type value with a positive sign
- The values lie between 0.0 and 1.0
- Random numbers generated by this method is of double types only
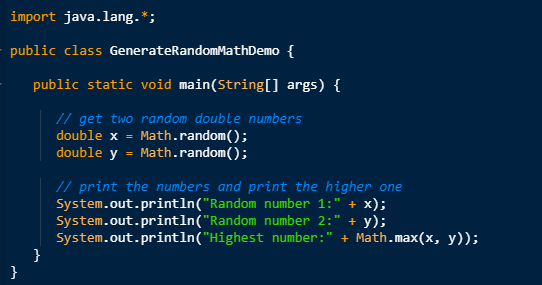
Let’s have a look at the code which demonstrates random number generation by using Math.Random() method.

Output:

Another example:
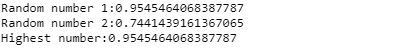
Output:
Generate Random Numbers Using java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom class
This is a utility class is used to generate random numbers of type int, doubles, boolean, etc. It improves performance and is used for jdk 1.7 and onward.
Below program demonstrate how we use the above class to generate a random number.
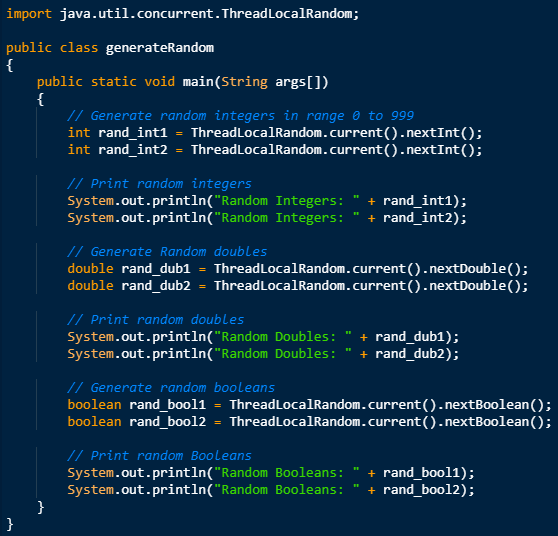
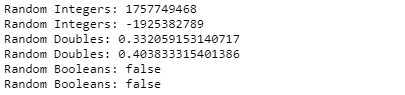
Output:
Random Number Generation in Java between Two Numbers:
We can simply generate random number between range a range by using Math.Random() and java.util.Random. Let us generate random number between 0 and 10 with the code below.
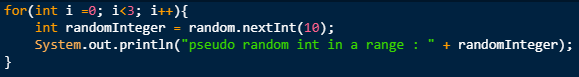
Output:
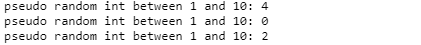
In the above code 0 is inclusive and 10 is exclusive. As mentioned previously in the discussion the above code is using Math.Random() method which returns pseudo-random number between the range of 0.0 to 1.0, where later one is exclusive, by multiplying output with and convert into integer, we can generate random integers in any range. If you need random number between any other two numbers e.g. between 0 and 100, just multiply output of random () method with 100 and then cast it into integer result.Conclusion:
- We can generate random number in java by using java.util.Random class, Math.Random () method, and ThreadLocalRandom which is available only for Java 7.
- Random class can generate data types which include integer, double, float, boolean, etc.
- Math.Random () method can only generate double value >= 0.0 and < 1.0.
- Math.random() is a thread safe method and can be called form multiple threads but its good idea to have separate random numbergenerators for separate thread to reduce contention. ThreadLocalRandom from Java 1.7 could be another choice if you are sharing your Random number generator among multiple threads.
- Efficient and convenient way to create random number generator in java is Math.Random() method.
Write a comment